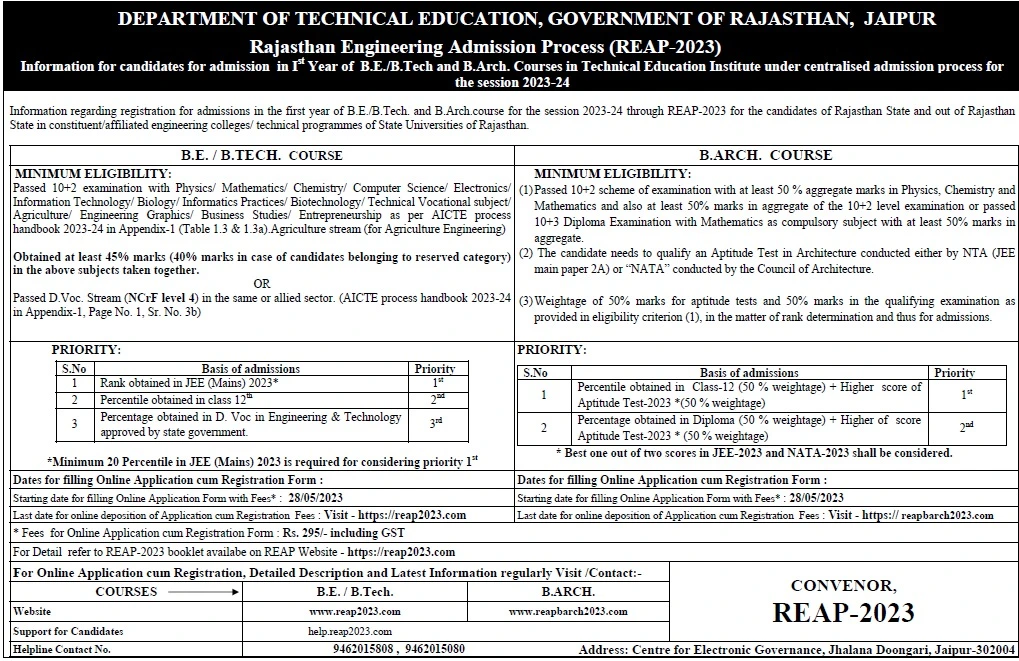
About the Department:
Our Department is one of the leading departments in this campus providing highly technology-oriented programmes to meet today's needs of young minds, a department having highly qualified, experienced, and dedicated teaching faculty to impart knowledge in various fields including recent technologies helping students to take on any problem related to Computer Science & Engineering.
With the right mix of creative talents, use of innovative technologies and strong relationships with various industries, the Department delivers quality methods of teaching that help students enhance their knowledge, understand the importance of being leaders in the area of their interest, and provide them with an unbeatable edge to success in today's demanding work place and global market.
India will soon be blooming into a developed and a prosperous country attaining a super- power status. An important premise of this vision is a demographic prediction that India will be a country of young people, who will take away from the developed countries the role of world's predominant work force. The sustenance of this role depends upon the work force acquiring the requisite skills, befitting the changed environment. Herein comes the role of providing right set of technical skills and help the youth to develop these skills. The students of B-Tech course are store houses of raw talents which need to be channelized and to a large extent this responsibility is shouldered by the faculty of the Department of Computer Science & Engineering by providing a foundation in shaping the personality of the future engineers. To keep in touch with the developments, the Department of Computer Science & Engineering organizes Workshops and Seminars from time to time.
Vision And Mission:
Vision: To produce graduates with Strong Fundamentals in the area of Computer Science and Engineering and to meet the needs of the society and industry in Self-Sustainable Manner with Ethical values.
Mission:
1. To deliver resources in IT-enabled domains by fostering a progressive academic environment that nurtures creativity, innovation, and technical skills through effective industry interaction and project-based learning.
2.To motivate students toward employability, entrepreneurship, research, and higher education by enhancing teaching-learning processes in a collaborative and intellectually stimulating atmosphere, guided by integrity, positive thinking, and social development.
3.To equip students with excellent engineering skills by providing a state-of-the-art infrastructure, value-added certification courses, and industry-oriented training, ensuring they become globally competitive professionals capable of solving real-world Challenges.
HOD Message:
Our department, founded on the principles of innovation, integrity, and inclusivity has always strived to provide a dynamic and supportive learning environment for our students. We believe that computer science is not just a field of study but a driving force for societal progress and transformation.
Academically we are designed to foster critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills. Our faculty members, who are experts in their respective fields, are dedicated to mentoring students and guiding them towards academic and professional success.
We have established state-of-the-art laboratories and research centres that facilitate cutting-edge research in various domains of computer science. Our faculty and students actively engage in research projects that address real-world challenges and contribute to the advancement of technology.
HOD, Computer Science & Engineering
a) Focus Area:
Computer science & Engineering focuses on the development and testing of software and software systems. It involves working with:
b) EFFORTS BY OUR FACULTIES:
Faculties take extra care of the students the knowledge delivery process throughout the course period. These dedicated and concentrated efforts have culminated in obtaining 100 % results. For these best results our faculty ensures complete learning of the student by providing:
DIGITAL NOTES:
The Department has digital notes with videos as well as hard copy Notes on all the subjects relevant to RTU syllabus. These notes have been prepared by experienced faculty. The Digital notes can be found on www.aryanotes.com.
STUDENT DEVELOPMENT (SDC) AND CAMPUS RECRUITMENT TRAINING (CRT):
The Student Development Centre (SDC) aims to enhance students' personal and professional growth through various skill-building programs. Campus Recruitment Training (CRT) prepares students for successful job placements by equipping them with essential interview and career skills. Together, SDC and CRT play a vital role in shaping well-rounded and industry-ready graduates.
Syllabus & Scheme
| S.No. | Description | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | III and IV Semester | View |
| 2 | V and VI Semester | View |
| 3 | VII and VIII Semester | View |








Departmental Lab's:
The department has following well- equipped laboratories that offer more that the prescribed practical needs as per RTU Curriculum :
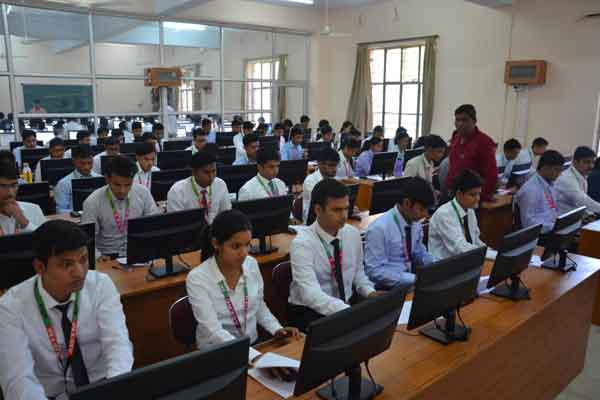

Operating System Simulation Lab
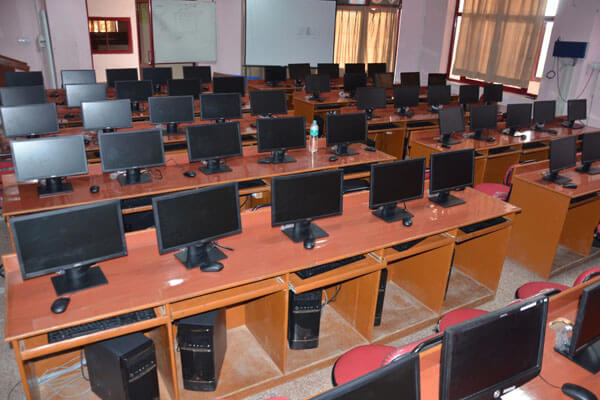

Compiler Design Lab
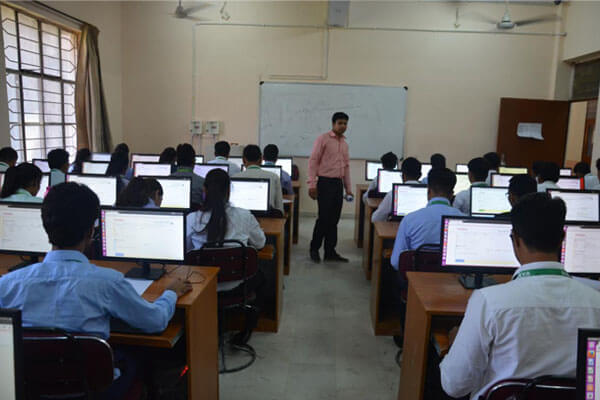

C Programming Lab

Project Lab /R&D Lab

FPGA Lab

Database Lab

Linux And Network Programming Lab

Java Programming Lab
List of Program Educational Objectives (PEO)
PEO-1
Graduate students will have thorough knowledge in science and engineering disciplines and have broad-based education in areas of computer science, including hardware, software learning in the structural form of course and curriculum.
PEO-2
Graduates will have solid foundation in engineering field required to solve computing problems using various programming languages and software’s/tools, and students can solve problems through logical and analytical thinking.
PEO-3
Graduates will be trained with good engineering breadth so as to comprehend, analyze, design, and create novel products and solutions for the real-life problem and as per the industry requirements by bridging extra certification courses.
PEO-4
To develop the professional and ethical attitude, effective communication skills and lateral learning for multidisciplinary approach, and an ability to relate engineering issues to broader social context.
PEO-5
To develop the academic environment and persue excellence in leadership, teamwork and skills for lifelong learning needed to persue successful professional career through structured learning, independent self studies, projects, industrial training, Seminars and Internships etc.
List of Program Outcomes
PO-1
Engineering Knowledge:
Apply knowledge of mathematics and science, with fundamentals of Engineering to be able to solve complex engineering problems related.
PO-2
Problem Analysis:
Identify, Formulate, review research literature and analyze complex engineering problems and reaching substantiated conclusions using first principles of mathematics, natural sciences and engineering sciences
PO-3
Design/Development of solutions:
Design solutions for complex engineering problems and design system components or processes that meet the specified needs with appropriate consideration for the public health and safety and the cultural societal and environmental considerations.
PO-4
Conduct Investigations of Complex problems:
Use research–based knowledge and research methods including design of experiments, analysis and interpretation of data, and synthesis of the information to provide valid conclusions.
PO-5
Modern Tool Usage:
Create, Select and apply appropriate techniques, resources and modern engineering and IT tools including prediction and modeling to complex engineering activities with an understanding of the limitations.
PO-6
The Engineer and Society:
Apply Reasoning informed by the contextual knowledge to assess societal, health, safety, legal and cultural issues and the consequent responsibilities relevant to the professional engineering practice.
PO-7
Environment and Sustainability:
Understand the impact of the professional engineering solutions in societal and environmental contexts sustainable development.
PO-8
Ethics:
Apply Ethical Principles and commit to professional ethics and responsibilities and norms of the engineering practice
PO-9
Individual and Team Work:
Function effectively as an individual and as a member or leader in diverse teams and in multidisciplinary Settings.
PO-10
Communication:
Communicate effectively on complex engineering activities with the engineering community and with society at large such write effective reports and design documentation, make effective presentations and give and receive clear instructions.
PO-11
Project Management and Finance:
Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of the engineering management principles and apply these to one’s own work, as a member and leader in a team, to manage projects and in multi disciplinary environments.
PO-12
Life-Long Learning:
Recognize the need for and have the preparation and ability to engage in independent and life-long learning the broadest context of technological change.
Program Specific Outcome
PSO-1:
Knowledge Enhancement in Computing:-
The ability to interpret the foundation and strategy of hardware and software of computer systems. Graduates can solve the problems in the areas related to algorithms, multimedia, data analytics, cloud computing, human computer interface, robotics, artificial intelligence and networking for efficient design of computer systems.
PSO-2 :
Software Design and Development:-
The ability to understand the software development lifecycle and methodologies of software systems. Graduate will learn competent skills and knowledge of software design process. Graduate will be acquaintance to practical proficiency with a broad area of programming concepts.
Course Outcomes (COs)
| S.No. | Course Code | Course Title | Course Outcomes (COs) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3CS2- 01 |
Advanced Engineering Mathematics | CO 1: | To learn the concepts and principles of Random variables. |
| CO 2: | To learn the concepts and principles of Probability distribution. | |||
| CO 3: | To learn the formulation of different mathematical problems into optimization Problems. | |||
| CO 4: | Apply the principles of optimization using differential calculus. | |||
| CO 5: | To understand the concepts of Liner Programming and the relation between demand and supply. Also, to learn the concepts of production and cost analysis. | |||
| 2 | 3CS1- 03 |
Managerial Economics and Financial Accounting | CO 1: | Graduates gain the ability to apply the knowledge of managerial and economic concepts and the ability to apply the tools and techniques. |
| CO 2: | Ability to understand demand and supply analysis and to Know the implementation of demand forecasting methods for production decisions and cost analysis. | |||
| CO 3: | Ability to understand the production and cost analysis of the firm. Understanding of types of markets and pricing methods and understanding the techniques regarding long-term investment decisions. | |||
| CO 4: | Ability to understand the application of various ratios and methods of analyzing the firm to know the firm’s financial position in depth and to understand different techniques of capital budgeting. To be able to conduct inter-firm and intra-firm comparisions. | |||
| 3 | 3CS3- 04 |
Digital Electronics | CO 1: | Understand number systems, basic logic gates, Boolean algebra and derive digital logic circuits. |
| CO 2: | Classify various minimization techniques and choose the best for designing logic circuit | |||
| CO 3: | Define characteristics of logic families and calculate their parameters | |||
| CO 4: | Design combinational logic circuits such as adder, subtractor, multiplexer, and decoder. | |||
| CO 5: | Classify the different types of flip flops and design counters, and registers using flip flops. | |||
| 4 | 3CS4- 05 |
Data Structures and Algorithms | CO 1: | Design applications using stacks and various types of queues |
| CO 2: | Analyze and apply operations of linked lists and demonstrate their applications | |||
| CO 3: | Evaluate the computational efficiency of the principal algorithms for sorting, searching, and hashing. | |||
| CO 4: | Demonstrate operations on trees and discuss various types of Trees. | |||
| CO 5: | Identify, model, solve, and develop algorithms for real-life problems like shortest path and MST using graph theory. | |||
| 5 | 3CS4- 06 |
Object Oriented Programming | CO 1: | Describe the Object Oriented Programming paradigm with the concept of objects and classes. |
| CO 2: | Explain the memory management techniques using constructors, destructors, and pointers. | |||
| CO 3: | Classify and demonstrate the various Inheritance techniques. | |||
| CO 4: | Understand how to apply polymorphism techniques to the object-oriented problem. | |||
| CO 5: | Summarize the exception-handling mechanism, file-handling techniques, and Use of generic programming in Object-oriented programming | |||
| 6 | 3CS4- 07 |
Software Engineering | CO 1: | Understand and compare the various software engineering models and differentiate between verification & validation |
| CO 2: | Apply various estimation models to determine the cost of software projects and illustrate risks in the software projects | |||
| CO 3: | Identify the requirements, design the SRS, and model various data flow and control flow diagrams | |||
| CO 4: | Learn various approaches to breaking down software into modules and create documentation | |||
| CO 5: | Describe object-oriented programming concepts to show class and object relationships | |||
| 7 | 3CS4-21 | Data Structures and Algorithms Lab |
CO 1: | Understand the concept of array storage and Examine the concept of row-major and column-major order. |
| CO 2: | List and Illustrate the implementation of basic data structure using an array. | |||
| CO 3: | Compare various searching techniques using arrays | |||
| CO 4: | Use linear and non-linear data structures like stacks, queues, linked lists, trees, etc. | |||
| CO 5: | Design and Formulate different sorting algorithms | |||
| 8 | 3CS4-22 | Object-Oriented Programming Lab |
CO 1: | Create and explain Basic C++ Programs using i/o variables and structures. |
| CO 2: | Apply object-oriented programming concepts using class and objects | |||
| CO 3: | Design and assess the classes for code reuse | |||
| CO 4: | Analyse and Apply the generic classes concepts in programming problem | |||
| CO 5: | Illustrate and evaluate the file Input Output mechanisms | |||
| 9 | 3CS4-23 | Software Engineering Lab |
CO 1: | Understand and Describe the basic concept of UML, design, implementation of test cases, and OOP concepts using Java. |
| CO 2: | Discuss and Analyse how to develop software requirements specifications for a given problem. | |||
| CO 3: | Explain and build DFD models. | |||
| CO 4: | Understand and develop various structure and behavior UML diagrams. | |||
| CO 5: | Explain the knowledge of the project management tool Demonstrate how to manage files using the projectLibre project management tool. | |||
| 10 | 3CS4-24 | Digital Electronics Lab |
CO 1: | Define different types of logic gates, identify their ICs, and also verify their truth table. |
| CO 2: | Derive basic logic gates, adders, and subtractors using universal gates. | |||
| CO 3: | Illustrate the realization of Boolean expression in SOP and POS form and design it using logic gates. | |||
| CO 4: | Design and test combinational circuits and develop sequential circuits. | |||
| CO 5: | Demonstrate team‐based laboratory activities with fellow students to interact effectively on a social and interpersonal level. | |||
| 11 | 3CS7-30 | Industrial Training |
CO 1: | Identify the problem in the relevant engineering fields and gather information through independent or collaborative study |
| CO 2: | Apply and summarize the knowledge of Mathematics, Science, and Engineering Fundamentals in the identified field of study | |||
| CO 3: | Apply the acquired skills in communication, writing, and engineering tools | |||
| CO 4: | Develop a product based on the experiences and projects carried out with the ability to work as an individual and in a group with the capacity to be a leader or manager as well as an effective team member | |||
| CO 5: | Demonstrate the professional and ethical responsibilities of an engineer. | |||
| 12 | 4CS2- 01 |
Discrete Mathematics Structure | CO 1: | Understand the basic principles of sets and operations in sets |
| CO 2: | Demonstrate the ability to write and evaluate a proof or outline the basic structure of and give examples of each proof technique described | |||
| CO 3: | Apply counting principles to determine probabilities. | |||
| CO 4: | Demonstrate an understanding of relations and functions and be able to determine their properties | |||
| CO 5: | Demonstrate different traversal methods for trees and graphs | |||
| 13 | 4CS1- 02 |
Technical Communication | CO 1: | Recall and identify four basic LSRW skills for learning technical communication. |
| CO 2: | Read, understand, and summarize the technical texts and documents. | |||
| CO 3: | Apply technical style in writing and note-making. | |||
| CO 4: | Compose official notes, letters, emails, resumes, job applications, and MOM with the usage of advanced grammar. | |||
| CO 5: | Design, analyze, and evaluate technical reports, articles, and proposals in proper format. | |||
| 14 | 4CS3- 04 |
Microprocessor & Interfaces |
CO 1: | Describe the general architecture of the 8085 microprocessor and differentiate between microprocessors and microcontrollers. Illustrate the demultiplexing of address/data bus and memory mapping of 8085 |
| CO 2: | Classify the instruction set of the 8085 microprocessor and demonstrate programming proficiency using various addressing modes. | |||
| CO 3: | Design counters with appropriate time delays and also categorize the interrupts of 8085 on various levels of functionality | |||
| CO 4: | Design 8085 microprocessor-based circuits for various applications by interfacing selected peripheral ICs (8255, 8259, 8254, and 8279). | |||
| CO 5: | Interfacing of Scanned multiplexed display, USART, RS232C, and RS422A with 8085 microprocessor. | |||
| 15 | 4CS4- 05 |
Database Management System |
CO 1: | Understand the basic concept of the database management system and analyze a given database application scenario to use the ER model for the conceptual design of the database |
| CO 2: | Understand the concept of relational algebra, and Apply SQL to find solutions to a broad range of queries | |||
| CO 3: | Apply normalization technique to improve database design | |||
| CO 4: | Understanding the concept of transaction processing | |||
| CO 5: | Demonstrate an understanding of concurrency control and database failure | |||
| 16 | 4CS4- 06 |
Theory of Computation | CO 1: | Define and discuss the concept of formal grammar, formal language, regular expression, and automata machine. |
| CO 2: | Design finite automata and push-down automata (PDA) machines for given formal languages or computational real-world problem statements. | |||
| CO 3: | Understand the capability of the Turing machine and design the Turing Machine for context-sensitive languages or computational real-world problem statements. | |||
| CO 4: | Choose and design appropriate automata for modeling the solution for various computational engineering problems. | |||
| CO 5: | Understand the concepts of tractable & untractable problems and be able to decide whether a given problem is tractable or not. | |||
| 17 | 4CS4-07 | Data Communication and Computer Networks |
CO 1: | Understand and Contrast the concept of Signals, OSI & TCP/IP reference models and discuss the functionalities of each layer in these models. |
| CO 2: | Design subnets and calculate the IP addresses to fulfill the network requirements of an organization | |||
| CO 3: | Analyze and apply various routing algorithms to find the shortest paths for packet delivery | |||
| CO 4: | Explain the details of Transport Layer Protocols (UDP, TCP) and suggest appropriate protocols for reliable/unreliable communication. | |||
| CO 5: | Analyze the features and operations of various application layer protocols such as HTTP, DNS, and SMTP. | |||
| 18 | 4CS4-21 | Microprocessor & Interfaces Lab |
CO 1: | Identify relevant information in order to supplement to the Microprocessor course. |
| CO 2: | Discuss programming strategies and select proper mnemonics and run their program on the 8085 microprocessor based training boards. | |||
| CO 3: | Show programming proficiency by writing the code in a well structured document and evaluate possible causes of discrepancy in practical experimental observations. | |||
| CO 4: | Develop testing and experimental procedures for 8085 Microprocessor applications and will analyze their operation under different conditions. | |||
| CO 5: | Demonstrate the ability to interact effectively on a social and interpersonal level with fellow students, and will demonstrate the ability to divide up and share task responsibilities to complete assignments. | |||
| 19 | 4CS4-22 | Database Management System Lab | CO 1: | Illustrate the ER model and identify the roles and privileges of various users in a database. |
| CO 2: | Apply common SQL statements using DDL, DML & DCL statements to perform various operations. | |||
| CO 3: | Construct SQL queries for various operations in a database. | |||
| CO 4: | Interpret Embedded and Nested queries. | |||
| CO 5: | Assess the need to create triggers and views to manage the database. | |||
| 20 | 4CS4-23 | Network Programming Lab | CO 1: | Define the fundamentals of underlying principles of computer networking. |
| CO 2: | Understand the key topologies that support the internet and Create a socket and analyze different client-server models. | |||
| CO 3: | Demonstrate the installation and configuration of the network simulator. | |||
| CO 4: | Applying the Network routing algorithm and evaluating the process of implementing simple routed internetwork. | |||
| CO 5: | Evaluate the error using various error-correcting techniques. | |||
| 21 | 4CS4-24 | Linux Shell Programming Lab | CO 1: | List the basic commands of the UNIX operating system and use them in a Linux environment (ubuntu, Fedora, etc.). |
| CO 2: | Understand commands related to process control and apply them to manage processes. | |||
| CO 3: | Understand the concepts of control structure, loops, cases, and functions in shell programming and apply them to create shell scripts. | |||
| CO 4: | Associate the concepts of arrays with Linux and apply them to create, compile, and execute C programs in a Linux terminal. | |||
| CO 5: | Compare different editors (vi, gedit, nano) and use them to create a shell script and C program for a given problem. | |||
| 22 | 4CS4-25 | Java Lab | CO 1: | Describe object-oriented concepts, java program structure, and its installation. |
| CO 2: | Demonstrate Object-oriented constructs such as various class hierarchies, interfaces, and Packages. | |||
| CO 3: | Develop and understand Exception handling. | |||
| CO 4: | To understand the concepts of threads and I/O in Java. | |||
| CO 5: | Able to build dynamic user interfaces using applets and Event handling in Java. | |||
| 23 | 5CS3-01 | Information Theory and Coding | CO 1: | Describe the concept of information and entropy |
| CO 2: | Discuss channel and Source coding theorem and also examine source coding schemes for data compaction. | |||
| CO 3: | Analyze error detection and correction using linear block codes. | |||
| CO 4: | Generate cyclic codes and justify properties of Galois fields (GF) polynomials. | |||
| CO 5: | Design Convolutional encoders of different rates, code trees, trellis, and state diagrams. | |||
| 24 | 5CS4-02 | Compiler Design | CO 1: | Discuss the major phases of compilers and use the knowledge of the Lex tool |
| CO 2: | Develop the parsers and experiment with the knowledge of different parser designs without automated tools. | |||
| CO 3: | Describe intermediate code representations using syntax trees and DAG’s as well as use this knowledge to generate intermediate code in the form of three address code representations. | |||
| CO 4: | Classify various storage allocation strategies and explain various data structures used in symbol tables | |||
| CO 5: | Summarize various optimization techniques used for dataflow analysis and generate machine code from the source code of a novel language. | |||
| 25 | 5CS4-03 | Operating Systems | CO 1: | Describe the basics of the operating systems, and mechanisms of OS to handle processes, threads, and their communication. |
| CO 2: | Analyze the memory management and its allocation policies. | |||
| CO 3: | Illustrate different conditions for deadlock and their possible solutions. | |||
| CO 4: | Discuss the storage management policies concerning different storage management technologies | |||
| CO 5: | Evaluate the concept of the operating system concerning UNIX, Linux, Time, and mobile OS. | |||
| 26 | 5CS4-04 | Computer Graphics and Multimedia | CO 1: | Understand and apply basics about computer graphics along with graphics standards. |
| CO 2: | Explain and analyze various algorithms to scan, and convert the basic geometrical primitives, Area filling. | |||
| CO 3: | Explain, illustrate, and design various algorithms for 2D transformations and clipping. | |||
| CO 4: | To understand the fundamental concepts of parallel and perspective projections and evaluate various algorithms for 3D transformations. | |||
| CO 5: | Understand various color models in computer graphics systems and develop animated motions through OpenGL. | |||
| 27 | 5CS4-05 | Analysis of Algorithms | CO 1: | Describe asymptotic analysis concepts and use them to evaluate the time complexity of different algorithms. |
| CO 2: | Explain, apply, and analyze the divide and conquer, greedy method, and dynamic programming techniques to solve various engineering problems. | |||
| CO 3: | Discuss and use Branch and Bound, and pattern-matching algorithms. | |||
| CO 4: | Discuss randomized algorithms for min-cut and 2-SAT problems. | |||
| CO 5: | Understand the concepts of NP-Hard and NP-Complete problems. | |||
| 28 | 5CS5-11 | Wireless Communication | CO 1: | To List the different modes of communication and explain the evolution of different mobile communication technologies |
| CO 2: | Summarize the challenges of wireless transmission and different design models. | |||
| CO 3: | To illustrate the working of a cellular network and discuss issues related to cellular network design. | |||
| CO 4: | To Illustrate different digital modulation and noise handling techniques used in Wireless Communication. | |||
| CO 5: | Analyze multiple antenna techniques used in 4G mobile technology, MIMO, and apply the concept to create new research for future generations. | |||
| 29 | 5CS4-21 | Computer Graphics & Multimedia Lab | CO 1: | Understand and apply the various predefined functions for drawing various geometric shapes |
| CO 2: | Explain and analyze various algorithms to scan, and convert the basic geometrical primitives, transformations, Area filling, clipping | |||
| CO 3: | Explain, illustrate, and design various kinds of viewing and Projections. | |||
| CO 4: | To understand the fundamentals of animation, virtual reality, and its related technologies. | |||
| CO 5: | Define, explain, and apply various concepts associated with computer graphics to develop the animated game | |||
| 30 | 5CS4-22 | Compiler Design Lab | CO 1: | Understand the Lexical analyzer and use this knowledge to implement its various sub-functions for any regular language. |
| CO 2: | Create a Symbol table and implement its operations in C language. | |||
| CO 3: | Define the ex tool and determine various tokens using it. | |||
| CO 4: | Examine the string for the given regular expression and evaluate an expression using the YACC Tool. | |||
| CO 5: | Understand the concept of Context-Free Grammar and break down the given grammar for calculating First. | |||
| 31 | 5CS4-23 | Analysis of Algorithms Lab | CO 1: | Compute running time and analyze the performance using Asymptotic Analysis. |
| CO 2: | Discuss various sorting, searching, and Graph Traversal algorithms and implement them. | |||
| CO 3: | Explain the divide-and-conquer paradigm and apply it to various problems. | |||
| CO 4: | Create programs for finding spanning trees, and shortest paths using different design techniques. | |||
| CO 5: | Describe various design techniques and compare them. | |||
| 32 | 5CS4-24 | Advance Java Lab | CO 1: | List all UI components Create UI widgets and apply event handling using Abstract Windowing Toolkit (AWT) & Swings |
| CO 2: | Discuss and Apply Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) to access databases through Java Programs | |||
| CO 3: | Analyze and Formulate remote methods in an application using Remote Method Invocation(RMI) | |||
| CO 4: | Select and create an appropriate multi-tier approach from stateful, stateless, and entity beans | |||
| CO 5: | Build dynamic web pages, using Servlets and JSP. | |||
| 33 | 5CS7-30 | Industrial Training | CO 1: | Identify the problem in the relevant engineering fields and gather information through independent or collaborative study |
| CO 2: | Apply and Summarize the knowledge of Mathematics, Science, and Engineering Fundamentals in the identified field of study | |||
| CO 3: | Apply the acquired skills in communication, writing, and engineering tools | |||
| CO 4: | Develop a product based on the experiences and projects carried out with the ability to work as an individual and in a group with the capacity to be a leader or manager as well as an effective team member | |||
| CO 5: | Demonstrate the professional and ethical responsibilities of an engineer. | |||
| 34 | 6CS3-01 | Digital Image Processing | CO 1: | Identify the fundamental elements of an image and Describe the need for digital image processing. |
| CO 2: | Understand different types of image transformation techniques and their properties. | |||
| CO 3: | Use various noise models and Calculate the values for restoration and degradation models. | |||
| CO 4: | Analyze and Evaluate various image compression techniques. | |||
| CO 5: | Integrate and Demonstrate various Image Transformation and Segmentation Techniques | |||
| 35 | 6CS4-02 | Machine Learning | CO 1: | Understand different types of machine learning techniques and their applications in the real world. |
| CO 2: | Apply various mathematical models for supervised machine learning models. | |||
| CO 3: | Apply and evaluate the unsupervised machine learning models through various clustering algorithms. | |||
| CO 4: | Apply reinforcement learning algorithms to solve real-time complex problems with an understanding of the trade-offs involved. | |||
| CO 5: | Design the recommendation system using natural language processing and evaluate the machine learning models through ANN. | |||
| 36 | 6CS4-03 | Information Security System | CO 1: | Identify services that enhance the security and its mechanism. |
| CO 2: | Classify security attacks on information over the network. Describe and apply classical encryption techniques. | |||
| CO 3: | Compare conventional encryption algorithms & public key cryptography, and design an Encryption algorithm to provide the Integration and confidentiality of a message. | |||
| CO 4: | Understand the concept of hash function with application and message authentication code in security system | |||
| CO 5: | Classify key management schemes and discuss web security and transport-level security protocols. | |||
| 37 | 6CS4-04 | Computer Architecture and Organisation | CO 1: | Understand the basic operations of digital computer systems to learn the integrated circuits |
| CO 2: | Describe arithmetic logic and shift micro-operations in symbolic form at a register transfer level. | |||
| CO 3: | Develop the assembly language programming and demonstrate the addressing modes used in instructions. | |||
| CO 4: | Analyze and measure clock periods, performance, and instruction throughput of single-cycle, multi-cycle, and pipelined implementations of a simple instruction set. | |||
| CO 5: | Apply algorithms for arithmetic operations and implementation for ALU design Classify and design different memory organization | |||
| 38 | 6CS4-05 | Artifical Intlligence | CO 1: | Compare different AI search techniques and apply them to real-world problems |
| CO 2: | Apply basic principles of AI in solutions that require problem-solving, inference, perception, knowledge representation, and reasoning | |||
| CO 3: | Develop intelligent algorithms for constraint satisfaction problems and also design intelligent systems for Game Playing | |||
| CO 4: | Classify different learning paradigms and its application in Neural Network | |||
| CO 5: | Explain concepts of Natural Language processing and discuss Expert System | |||
| 39 | 6CS4-06 | Cloud Computing | CO 1: | Recall and summarize the basic concepts of cloud computing |
| CO 2: | Discuss the architectural design of the cloud and illustrate various programming models. | |||
| CO 3: | Outline the virtualization technology and determine its uses. | |||
| CO 4: | Explain the basic threats and security mechanisms in the cloud | |||
| CO 5: | Summarize the cloud available platforms for business and industry perspective | |||
| 40 | 6CS5-11 | Distributed System | CO 1: | List basic components of the distributed system and describe various issues of DS. |
| CO 2: | Illustrate and analyze process management and inter-process Communication techniques. | |||
| CO 3: | Compare Distributed File Systems, and Distributed Process Scheduling with Transaction Services and Concurrency Control. | |||
| CO 4: | Analyze Distributed Shared Memory with memory consistency models and models of distributed computation. | |||
| CO 5: | Demonstrate different algorithms and techniques for Distributed Agreement and replicated Data Management. | |||
| 41 | 6CS4-21 | Digital Image Processing Lab |
CO 1: | Describe digital image representation, and manipulation and Illustrate the use of histograms. |
| CO 2: | Applying various Geometric transformations on image and Illustrate Two- dimensional Fourier transform. | |||
| CO 3: | Use and Compare, various Linear filtering methods. | |||
| CO 4: | Applying various Ideal filters in the frequency domain and Understanding the concept of edge detection. | |||
| CO 5: | Compose various Morphological operations on binary images and Generate their transformed images. | |||
| 42 | 6CS4-22 | Machine Learning Lab | CO 1: | Understand the mathematical and statistical prospects of machine learning algorithms through Python programming. |
| CO 2: | Design and evaluate the unsupervised models through Python inbuilt functions. | |||
| CO 3: | Design and apply various reinforcement algorithms to solve real-time complex problems. | |||
| CO 4: | Design and develop the code for the recommender system using Natural Language processing | |||
| CO 5: | Understand the basic concepts of deep neural network model and design the same. | |||
| 43 | 6CS4-23 | Python Lab | CO 1: | List various data types in Python and use them to solve basic Python programs. |
| CO 2: | Describe Conditional statements and Looping structures concepts in Python and apply these to create searching and sorting programs. | |||
| CO 3: | Explain the usage of Lists, Tuples, Set, Dictionary, and Strings and use these to solve programming problems in different ways. | |||
| CO 4: | Understand various built-in Python functions and formulate user-defined functions. | |||
| CO 5: | Discuss file-handling concepts and apply them to create basic data-handling programs. | |||
| 44 | 6CS4-24 | Mobile Application Development Lab |
CO 1: | Discuss the components and different Layout for mobile application development framework for android |
| CO 2: | Design a Simple GUI application with the Use of Built-in components and widgets. | |||
| CO 3: | Define a solution for complex problems | |||
| CO 4: | Create databases to store application data locally. | |||
| CO 5: | Test and Show the results on emulators or physical handheld devices | |||
| 45 | 7CS4-01 | Internet of Things | CO 1: | Understand the basics of application areas of IOT |
| CO 2: | Explain and realize the revolution of the Internet in Mobile Devices, Cloud & Sensor Networks | |||
| CO 3: | Discuss the architecture, operation, and business benefits of an IoT solution | |||
| CO 4: | Examine the potential business opportunities that IoT can uncover | |||
| CO 5: | Explore the relationship between IoT, cloud computing, and big data and Identify how IoT differs from traditional data collection systems | |||
| 46 | 7ME6-60.2 | Quality Management | CO 1: | Describe the concepts of Quality, and evaluate various philosophies of quality gurus, cost of quality, and quality control. |
| CO 2: | Analyses and interprets the process quality using various QC tools like control chart acceptance Sampling, Analysis of variance (ANOVA), and design of experiments (DOE). | |||
| CO 3: | Describe as scope of benchmarking, Six Sigma Technique, and ISO standards and manage quality programs. | |||
| CO 4: | Interpret the process quality improvement using CFD robust design and the Taguchi method. | |||
| CO 5: | Analyses the design failure and Implementation of the effects. | |||
| 47 | 7CS4-21 | Internet of Things Lab | CO 1: | Explain the concept and Application of the Internet of Things |
| CO 2: | Illustrate key technologies, protocols, and standards in the Internet of Things. | |||
| CO 3: | Analyze trade-offs in interconnected wireless embedded device networks | |||
| CO 4: | Application of IoT in the automation of Commercial and Real-World examples | |||
| CO 5: | Design a simple IOT system comprising sensors, edge devices, and wireless network connections involving prototyping, programming, and data analysis. | |||
| 48 | 7CS4-22 | Cyber Security Lab | CO 1: | Apply the cryptographic algorithms for data communication. |
| CO 2: | Understand the implementation of various security tools and algorithms. | |||
| CO 3: | Apply the Digital signature for secure data transmission and secure data storage. | |||
| CO 4: | Utilize the different open-source tools for network security and analysis. | |||
| CO 5: | Demonstrate intrusion detection system using network security tool. | |||
| 49 | 7CS7-30 | Industrial Training |
CO 1: | Identify the problem in the relevant engineering fields and gather information through independent or collaborative study |
| CO 2: | Apply and summarize the knowledge of Mathematics, Science, and Engineering Fundamentals in the identified field of study | |||
| CO 3: | Apply the acquired skills in communication, writing, and engineering tools | |||
| CO 4: | Develop a product based on the experiences and projects carried out with the ability to work as an individual and in a group with the capacity to be a leader or manager as well as an effective team member | |||
| CO 5: | Demonstrate the professional and ethical responsibilities of an engineer. | |||
| 49 | 7CS7-40 | Seminar | CO 1: | Identify emerging technologies/current trends to gather relevant information through independent or collaborative study. |
| CO 2: | Analyse and Summarize related work and literature in the identified field of study. | |||
| CO 3: | Design a clear, well-constructed document that represents both technical and non-technical information using engineering-standard figures, reports, and drawings. | |||
| CO 4: | Demonstrate effective oral presentations in given time constraints, using a variety of presentation media. | |||
| CO 5: | Develop listening skills and comprehend information, instructions, and viewpoints either as a presenter or as an audience. | |||
| 50 | 8CS4-01 | Big Data Analytics | CO 1: | Explain the building block of Big Data and overview of an exciting growing field of big data analytics |
| CO 2: | Understanding and Applying the programming aspects of map-reduce | |||
| CO 3: | Analyze pig architecture to make easier Hadoop programming | |||
| CO 4: | Applying Structure to Hadoop data with Hive | |||
| CO 5: | Design applications to solve complex real-world problems for decision support. | |||
| 51 | 8EE6-60.2 | Soft Computing | CO 1: | Ability to analyze and appreciate the applications that can use fuzzy logic |
| CO 2: | Ability to design inference systems | |||
| CO 3: | Ability to understand the difference between learning and programming and explore practical applications of Neural Networks (NN). | |||
| CO 4: | Ability to appreciate the importance of optimizations and its use in computer engineering fields and other domains | |||
| CO 5: | Students would understand the efficiency of a hybrid system and how Neural Networks and fuzzy logic can be hybridized to form a Neuro-fuzzy network and its various applications. | |||
| 52 | 8CS4-21 | Big Data Analytics Lab | CO 1: | Understand and implement the basics of data structures like Linked lists, stack, queue, set, and map in Java. |
| CO 2: | Demonstrate knowledge of big data analytics and implement different file management tasks in Hadoop. | |||
| CO 3: | Understand Map Reduce Paradigm and develop data applications using a variety of systems. | |||
| CO 4: | Analyze and perform different operations on data using Pig Latin scripts. | |||
| CO 5: | Illustrate and apply different operations on relations and databases using Hive. | |||
| 53 | 8CS4-22 | Software Testing and Validation Lab |
CO 1: | Understand the Automation Testing Approach using the JaBuTi Tool. |
| CO 2: | Analyse & Discuss the performance of different websites using JMeter | |||
| CO 3: | Describe & Calculate the mutation score for various programs using the jumble testing tool. | |||
| CO 4: | Calculate the coverage analysis of programs using the Eclemma tool. | |||
| CO 5: | Generate Test sequences and compare them using the Selenium tool for different websites. | |||
| 54 | 8CS7- 50 |
Project | CO 1: | Competence in applying software engineering principles in planning, formulating an innovative design/ approach, and computing the requirements appropriate to solve the problem within the context of legal, global, and environmental constraints. |
| CO 2: | Ability to plan, monitor, and manage project schedules, resources, and work assignments to ensure timely completion. | |||
| CO 3: | Ability to test and defend the performance of the implemented project and understand the Implications of the solution. | |||
| CO 4: | Perform professionally as a team member, accepting responsibility, taking initiative, and providing the leadership necessary to ensure Project success. | |||
| CO 5: | Ability to use formal and informal Communication with team members and guide, make presentations, and prepare technical documents. |
Placements
| B.Tech 2022-Batch | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placement List-2022 | |||||
| B.Tech 2021-Batch | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placement List-2021 | |||||
| B.Tech 2015-2016 Batch | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S.No. | Year | Name | Roll No. | Company Name | |
| 1 | 2015-2016 | VIKAS RATHI | 12EAIIT061 | TCS | |
| 2 | 2015-2016 | AASHISH RANJAN | 12EAIIT001 | Tech Mahindra | |
| 3 | 2015-2016 | AJAY BASNET | 12EAIIT002 | Tech Mahindra | |
| 4 | 2015-2016 | AMIT JEENGAR | 12EAIIT003 | Tech Mahindra | |
| 5 | 2015-2016 | AMIT YADAV | 12EAIIT004 | Tech Mahindra | |
| 6 | 2015-2016 | BANWARI LAL MEENA | 12EAIIT007 | Tech Mahindra | |
| 7 | 2015-2016 | MANISH GURAGAIN | 12EAIIT023 | Good Through Software | |
| 8 | 2015-2016 | BHAWANI SHANKER | 12EAIIT008 | Good Through Software | |
| 9 | 2015-2016 | RAJ KUMAR | 12EAIIT040 | Prolifics | |
| 10 | 2015-2016 | SHRUTI GARG | 12EAIIT052 | Prolifics | |
| 11 | 2015-2016 | SONALI SINGH | 12EAIIT055 | Collabera | |
| 12 | 2015-2016 | MOHIT SONI | 12EAIIT028 | Collabera | |
| 13 | 2015-2016 | NAZAR ULLA | 12EAIIT031 | Collabera | |
| 14 | 2015-2016 | RAHUL SHARMA | 12EAIIT039 | CMS IT Services Pvt. Ltd | |
| 15 | 2015-2016 | SHUCHITA SHARMA | 12EAIIT053 | CMS IT Services Pvt. Ltd | |
| 16 | 2015-2016 | KHUSHBOO BHATIA | 12EAIIT020 | Mphasis | |
| 17 | 2015-2016 | NEHA KUMARI | 12EAIIT032 | Mphasis | |
| 18 | 2015-2016 | NIDHI KHATRI | 12EAIIT033 | Mphasis | |
| 19 | 2015-2016 | NIRAJ KUMAR | 12EAIIT034 | Mphasis | |
| 20 | 2015-2016 | VEERAESHWAR CHANDER | 12EAIIT059 | Rose International | |
| 21 | 2015-2016 | ASHISH KUMAR JOSHI | 12EAIIT006 | Rose International | |
| 22 | 2015-2016 | MOHD ASIF | 12EAIIT027 | Rose International | |
| 23 | 2015-2016 | RAJAT PARIK | 12EAIIT041 | Rose International | |
| 24 | 2015-2016 | INDRA KUMAR DANGAL | 12EAIIT017 | Rose International | |
| 25 | 2015-2016 | ARUNA GAUTAM | 12EAIIT005 | Amar Ujala | |
| 26 | 2015-2016 | HARSHIT GUPTA | 12EAIIT016 | Capgemini | |
| 27 | 2015-2016 | BHUWAN CHHETRY | 12EAIIT009 | HCL Technologies | |
| 28 | 2015-2016 | SAMPAT KUMAR SHARMA | 12EAIIT044 | Adastra Softwares | |
| 29 | 2015-2016 | SANJEEV KUMAR SINGH | 12EAIIT045 | Adastra Softwares | |
| 30 | 2015-2016 | SANTOSH KUMAR | 12EAIIT046 | Adastra Softwares | |
| 31 | 2015-2016 | RAHUL BUNKAR | 12EAIIT038 | Adastra Softwares | |
| 32 | 2015-2016 | DILIP KUMAR | 12EAIIT013 | Arden Telecom | |
| 33 | 2015-2016 | GIREESH BABU HARIJAN | 12EAIIT015 | Arden Telecom | |
| 34 | 2015-2016 | MAYANK GARG | 12EAIIT024 | Cyfuture | |
| 35 | 2015-2016 | REKHA AGARWAL | 12EAIIT042 | Cyfuture | |
| 36 | 2015-2016 | SATISH KUMAR | 12EAIIT047 | Amazon | |
| 37 | 2015-2016 | JITENDER PAL SINGH | 12EAIIT018 | CADD Centre | |
| 38 | 2015-2016 | CHHITAR MAL VERMA | 12EAIIT010 | Asahi India Glass | |
| 39 | 2015-2016 | DEVENDRA JANGIR | 12EAIIT012 | Consultadd | |
| 40 | 2015-2016 | KARUNA YADAV | 12EAIIT019 | Consultadd | |
| 41 | 2015-2016 | PANKAJ KUMAR | 12EAIIT035 | HCL (TSS) | |
| 42 | 2015-2016 | PREM PRAKASH KUMHAR | 12EAIIT036 | HCL (TSS) | |
| 43 | 2015-2016 | RAGHUVEER BHADRU | 12EAIIT037 | HCL (TSS) | |
| 44 | 2015-2016 | SHIVEN CHOUDHARY | 12EAIIT049 | Dekho Network | |
| 45 | 2015-2016 | SHIVESH VATS | 12EAIIT050 | Dekho Network | |
| 46 | 2015-2016 | SOHAN LAL SHARMA | 12EAIIT054 | Dekho Network | |
| 47 | 2015-2016 | TARUN SINGH | 12EAIIT058 | Dekho Network | |
| 48 | 2015-2016 | DURGESH SUMAN | 12EAIIT014 | Dekho Network | |
| 49 | 2015-2016 | ROBIN RAJ | 12EAIIT043 | eUniversal | |
| 50 | 2015-2016 | VIKRAM KUMAR JHA | 12EAIIT063 | UniTech | |
| 51 | 2015-2016 | VISHVENDRA SINGH GURJAR | 12EAIIT064 | UniTech | |
| B.Tech 2014-2015 Batch | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S.No. | Year | Name | Roll No. | Company Name | |
| 1 | 2014-2015 | KUNIKA SHARMA | 11EAIIT036 | Unisys | |
| 2 | 2014-2015 | AAYUSH GUPTA | 11EAIIT002 | L&T Infotech | |
| 3 | 2014-2015 | ANJALI AGARWAL | 11EAIIT006 | L&T Infotech | |
| 4 | 2014-2015 | KANISHKA KHINCHI | 11EAIIT029 | L&T Infotech | |
| 5 | 2014-2015 | LATA LAKHWANI | 11EAIIT038 | L&T Infotech | |
| 6 | 2014-2015 | AKSHAY TIWARI | 11EAIIT004 | Concierge Tech. | |
| 7 | 2014-2015 | REETIKA CHOPRA | 11EAIIT070 | Concierge Tech. | |
| 8 | 2014-2015 | SHIVAM RAJPUT | 11EAIIT077 | Concierge Tech. | |
| 9 | 2014-2015 | RAHUL RANKAWAT | 11EAIIT065 | Concierge Tech. | |
| 10 | 2014-2015 | HARSHIT MITTAL | 11EAIIT024 | Cyber Futuristic | |
| 11 | 2014-2015 | MANAN PANDEY | 11EAIIT040 | Cyber Futuristic | |
| 12 | 2014-2015 | RADHIKA RAWAT | 11EAIIT062 | Cyber Futuristic | |
| 13 | 2014-2015 | SHARDUL NEGI | 11EAIIT073 | Cyber Futuristic | |
| 14 | 2014-2015 | KRATIKA SHARMA | 11EAIIT033 | Cyber Futuristic | |
| 15 | 2014-2015 | KULDEEP KUMAR | 11EAIIT034 | Cyber Futuristic | |
| 16 | 2014-2015 | TAPAN SAIN | 11EAIIT085 | Girnar Soft | |
| 17 | 2014-2015 | DHARAMVEER | 11EAIIT018 | CADD Centre | |
| 18 | 2014-2015 | DHEERAJ AMETA | 11EAIIT019 | CADD Centre | |
| 19 | 2014-2015 | DINESH KUMAR CHEJARA | 11EAIIT020 | CADD Centre | |
| 20 | 2014-2015 | DINESH YADAV | 11EAIIT021 | CADD Centre | |
| 21 | 2014-2015 | JAI PRAKASH | 11EAIIT027 | CADD Centre | |
| 22 | 2014-2015 | JAINUL SHAH | 11EAIIT028 | CADD Centre | |
| 23 | 2014-2015 | KHUSHBOO BANSHIWAL | 11EAIIT031 | CADD Centre | |
| 24 | 2014-2015 | KOUSHAL SINGH | 11EAIIT032 | CADD Centre | |
| 25 | 2014-2015 | SAKSHI PANJABI | 11EAIIT072 | Mindtree | |
| 26 | 2014-2015 | SHUBHAM PANDEY | 11EAIIT079 | Mindtree | |
| 27 | 2014-2015 | APURVA CHHAPARWAL | 11EAIIT009 | Collabera | |
| 28 | 2014-2015 | KAVYA BHATT | 11EAIIT030 | Collabera | |
| 29 | 2014-2015 | ANJALI SHARMA | 11EAIIT007 | Collabera | |
| 30 | 2014-2015 | PRIYANKA SOLANKI | 11EAIIT061 | Collabera | |
| 31 | 2014-2015 | RAHUL GUPTA | 11EAIIT063 | Collabera | |
| 32 | 2014-2015 | RAHUL KUMAR KOLI | 11EAIIT064 | Collabera | |
| 33 | 2014-2015 | SUBHAM KUMAR | 11EAIIT081 | IBM | |
| 34 | 2014-2015 | AAKASH SHARMA | 11EAIIT001 | Merchant Navy | |
| 35 | 2014-2015 | AKSHAY LAVA | 11EAIIT003 | Merchant Navy | |
| 36 | 2014-2015 | BHARTI NEGI | 11EAIIT015 | HCL | |
| 37 | 2014-2015 | NAKUL SINGH RATHORE | 11EAIIT045 | HCL | |
| 38 | 2014-2015 | NARESH JOSHI | 11EAIIT046 | HCL | |
| 39 | 2014-2015 | NEMI CHAND MEENA | 11EAIIT047 | HCL | |
| 40 | 2014-2015 | KULDEEP SHARMA | 11EAIIT035 | Adastra | |
| 41 | 2014-2015 | LAKSHYA SHARMA | 11EAIIT037 | Adastra | |
| 42 | 2014-2015 | MADAN LAL SOLANKI | 11EAIIT039 | Adastra | |
| 43 | 2014-2015 | MANISH TYAGI | 11EAIIT042 | Adastra | |
| 44 | 2014-2015 | MIHUL CHOUDHARY | 11EAIIT043 | Adastra | |
| 45 | 2014-2015 | MOIN KHAN | 11EAIIT044 | Adastra | |
| 46 | 2014-2015 | ATUL MODI | 11EAIIT011 | Adastra | |
| 47 | 2014-2015 | SHEERSHA VYAS | 11EAIIT075 | Adastra | |
| 48 | 2014-2015 | SURENDRA BHALWARA | 11EAIIT082 | Adastra | |
| 49 | <2014-2015 | SURESH KUMAR | 11EAIIT083 | Adastra | |
| 50 | 2014-2015 | VIJAY SINGH | 11EAIIT087 | Adastra | |
| 51 | 2014-2015 | YAMINI RAHURE | 11EAIIT089 | Adastra | |
| 52 | 2014-2015 | RAVI KANT AGARWAL | 11EAIIT067 | JK Techno soft | |
| 53 | 2014-2015 | RAVINDRA PATIDAR | 11EAIIT069 | JK Techno soft | |
| 54 | 2014-2015 | RAVI PANCHAL | 11EAIIT068 | JK Techno soft | |
| 55 | 2014-2015 | BHASKAR JYOTI MEDHI | 11EAIIT016 | I GATE | |
| 56 | 2014-2015 | CHANDAN LAKHERA | 11EAIIT017 | I GATE | |
| 57 | 2014-2015 | AKSHITA PAREEK | 11EAIIT005 | Amdocs | |
| 58 | 2014-2015 | ARCHANA BHARDWAJ | 11EAIIT010 | Academiaguru.com | |
| 59 | 2014-2015 | PRATIKA GUPTA | 11EAIIT057 | Academiaguru.com | |
| 60 | 2014-2015 | BAIJU KUMAR | 11EAIIT013 | Academiaguru.com | |
| 61 | 2014-2015 | NIRAJ KUMAR | 11EAIIT049 | Kukars | |
| 62 | 2014-2015 | NITESH KUMAR SALVI | 11EAIIT050 | Kukars | |
| 63 | 2014-2015 | PIYUSH MITTAL | 11EAIIT052 | Kukars | |
| 64 | 2014-2015 | PRASHANT KUMAR | 11EAIIT054 | Kukars | |
| 65 | 2014-2015 | PRATEEK GAUR | 11EAIIT055 | Kukars | |
| 66 | 2014-2015 | PRATEEK MATHUR | 11EAIIT056 | Kukars | |
| 67/th> | 2014-2015 | PRAVEEN JAIN | 11EAIIT058 | Kukars | |
| 68 | 2014-2015 | VIJAY BHARTI | 11EAIIT086 | Kukars | |
| 69 | 2014-2015 | SHUBHAM BANSAL | 11EAIIT078 | Kukars | |
| 70 | 2014-2015 | GAURAV JHA | 11EAIIT022 | Kukars | |
| 71 | 2014-2015 | VINOD KUMAR | 11EAIIT088 | Mobiloitte | |
| 72 | 2014-2015 | NIKITA MANRTI | 11EAIIT048 | Mobiloitte | |
| 73 | 2014-2015 | HARSHA SHARMA | 11EAIIT023 | Capgemini | |
| 74 | 2014-2015 | HARSHITA GALAV | 11EAIIT025 | Capgemini | |
| 69 | 2014-2015 | JAGDISH PRASAD KUMAWAT | 11EAIIT075 | Capgemini | |
| 76 | 2014-2015 | PRIYA | 11EAIIT060 | Avyukta | |
| 77 | 2014-2015 | RAJNISH KUMAR | 11EAIIT066 | Avyukta | |
| 78 | 2014-2015 | PARUL KHANDELWAL | 11EAIIT051 | HCL Talent Care | |
| 79 | 2014-2015 | RUBIYA KHAN | 11EAIIT071 | HCL Talent Care | |
| 80 | 2014-2015 | SHIKHA AHUJA | 11EAIIT076 | HCL Talent Care | |
| 81 | 2014-2015 | SUSHIL KUMAR | 11EAIIT084 | HCL Talent Care | |